Abstract
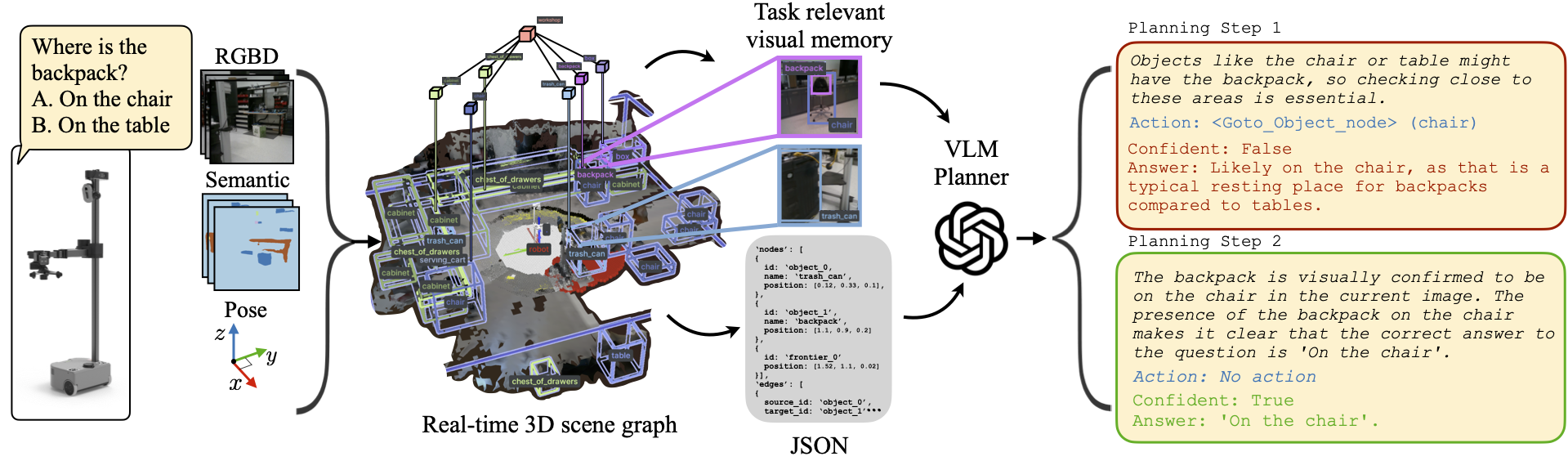
In Embodied Question Answering (EQA), agents must explore and develop a semantic understanding of an unseen environment to answer a situated question with confidence. This problem remains challenging in robotics, due to the difficulties in obtaining useful semantic representations, updating these representations online, and leveraging prior world knowledge for efficient planning and exploration. To address these limitations, we propose GraphEQA, a novel approach that utilizes real-time 3D metric-semantic scene graphs (3DSGs) and task relevant images as multi-modal memory for grounding Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to perform EQA tasks in unseen environments. We employ a hierarchical planning approach that exploits the hierarchical nature of 3DSGs for structured planning and semantics-guided exploration. We evaluate GraphEQA in simulation on two benchmark datasets, HM-EQA and OpenEQA, and demonstrate that it outperforms key baselines by completing EQA tasks with higher success rates and fewer planning steps. We further demonstrate GraphEQA in multiple real-world home and office environments.
Method
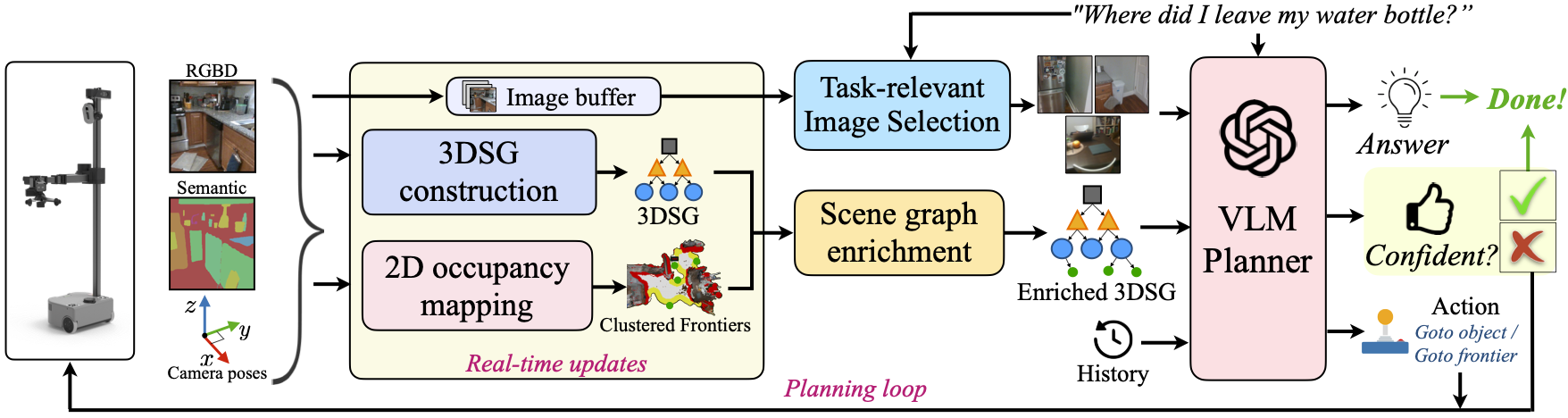
Overall GraphEQA architecture. As the agent explores the environment, it used its sensor data (RGBD images, semantic map, camera poses and intrinsics) to construct a 3D metric-semantic hierarchical scene graph (3DSG) as well as a 2D occupancy map for frontier selection in real time. The constructed 3DSG is then enriched with semantic room labels and semantically-enriched frontiers. From the set of images collected during each trajectory execution, a task-relevant subset is selected, called the task-relevant visual memory. A VLM-based planner takes as input the enriched scene graph, task-relevant visual memory, a history of past states and actions, and the embodied question and outputs the answer, its confidence in the selected answer, and the next step it needs to take in the environment. If the VLM agent is confident in its answer, the episode is terminated, else the proposed action is executed in the environment and the process repeats.
Hierarchical VLM Planner Architecture
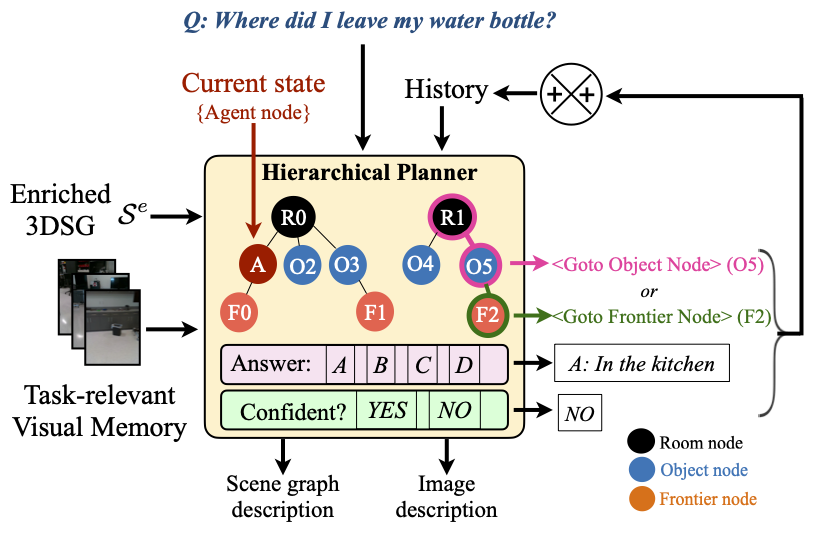
The Hierarchical Vision-Language planner takes as input the question, enriched scene graph, task-relevant visual memory, current state of the robot (position and room) and a history of past states, actions, answers and confidence values. The planner chooses the next Goto_Object_node action hierarchically by first selecting the room node and then the object node. The Goto_Frontier_node action is chosen based on the object nodes connected to the frontier via edges in the scene graph. The planner is asked to output a brief reasoning behind choosing each action. The planner also outputs an answer, confidence in its answer, reasoning behind the answer and confidence, the next action, a brief description of the scene graph and the visual memory.
Experimental Results
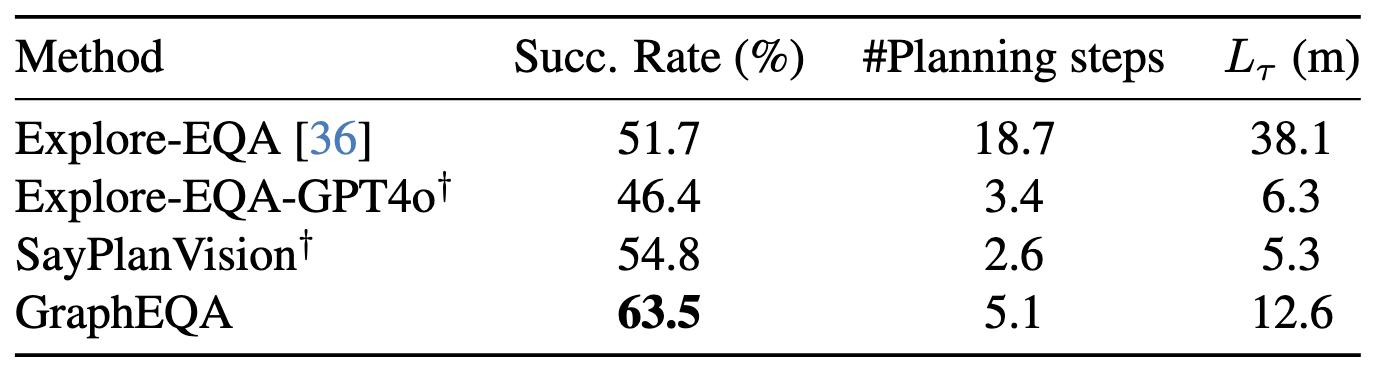
We compare the performance of GraphEQA against competitive baselines in simulation in the Habitat-Sim environment on the HM-EQA and OpenEQA datasets and in the real-world in two unique home environments. The above table shows comparison to baselines in simulation using metrics: average success rate (%), average number of VLM planning steps, and average trajectory length Lτ. We compare against several baselines and focus on methods that employ VLM-based planners for solving EQA or object goal navigation tasks. We compare against a strong baseline, Explore-EQA, which calibrates Prismatic-VLM to answer embodied questions confidently while maintaining a 2D semantic memory and using prompted images to guide exploration. Note that ExploreEQA is always executed for a prespecified maximum number of steps, with the highest confidence step chosen to answer the question, while GraphEQA terminates based on a confidence threshold. We implement additional variants of ExploreEQA with newer foundation models --- e.g., GPT4o, Llama 4 Maverick, and Gemini 2.5 Pro --- for fair comparison with respective VLM variants of GraphEQA. We also compare against SayPlanVision, a modified version of SayPlan, which in addition to the full scene graph also has access to task-relevant visual memory. We observe that GraphEQA has higher success rate as compared to Explore-EQA and Explore-EQA-GPT4o, without the need to build an explicit 2D semantic task-specific memory.
Compared to Explore-EQA, our method completes the task in significantly lower planning steps and navigates the environment more efficiently (lower trajectory length). GraphEQA outperforms SayPlanVision, without needing access to the complete scene graph. Qualitatively, we observe that given access to the complete scene graph, SayPlanVision is overconfident about its choice of object node actions, leading to shorter trajectory lengths in successful cases, but also to increased failure cases. Table 1 shows simulation results comparing GraphEQA to the above baselines on the HM-EQA and OpenEQA datasets. Overall, GraphEQA outperforms all other baselines. Compared to Explore-EQA, our method completes tasks in significantly fewer planning steps and with lower trajectory length, indicating more efficient navigation. We also observe that the GPT and Llama variants of Explore-EQA have lower success rates than Explore-EQA, with qualitative results indicating overconfidence in VLMs' predictions, leading to terminating episodes before exploring sufficiently. We note that Explore-EQA's Gemini variant performs better than Explore-EQA, likely due to the inherent spatial reasoning capabilities of Gemini 2.5 Pro. GraphEQA outperforms SayPlanVision even though SayPlanVision has access to the complete scene graph.